Women’s Workforce Participation State wise Trends in India
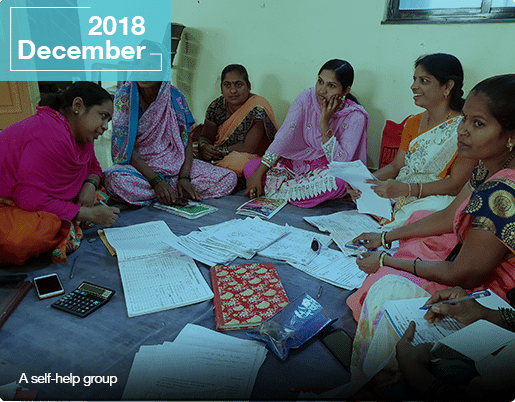
Madhya Pradesh (MP) is the only state in India to have witnessed a rise in workforce participation rates (WPRs) of women in both rural and urban areas between 2011-12 and 2017-18. The increase in women’s WPR in MP was driven largely by increase in self-employment in the rural areas and regular employment in the urban areas. According to the Periodic Labourforce Survey in 2017-18, more than half of the female workforce in the state is self-employed, with a higher incidence of self-employment in rural areas. While approximately 88 percent of the rural self-employed women in MP are engaged in unpaid work, the share of women in own account enterprises is substantially high in urban MP. The distribution of casual women workers suggests very few women engaged under MGNREGA and other public works as 96 percent women in casual employment were engaged in non-public works, with very little security or guarantee of payment