IWWAGE-Institute for What Works to Advance Gender Equality
From aspiration to empowerment: Impact of women’s collectives
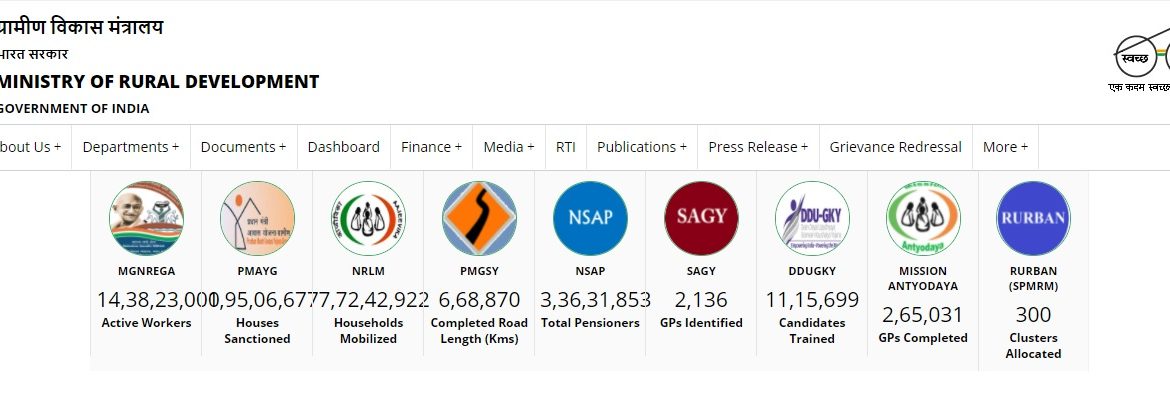
The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY NRLM) has adopted a focussed approach towards gender mainstreaming in its programme architecture. This includes establishing institutional mechanisms like Social Action Committees at the village organisation (VO SAC) and cluster federation levels to serve as response mechanisms to various issues that women and girls face, and that continue to act as barriers for them in accessing their rights and entitlements to lead a decent living. These Social Action Committees have shown exemplary leadership in strengthening the gender responsiveness of the programme at the grassroots level, especially during COVID-19.
The compendium on best practices titled, From aspiration to empowerment: Impact of women’s collectives, was launched in the presence of Sadhvi Niranjan Jyoti, Minister of State, Rural Development, officials from the Ministry of Rural Development and all State Governments through an online event, national webinar on sharing of best practices adopted for addressing gender issues by VO SACs held on June 29, 2021. The compendium of case studies from 23 States highlights the processes, mechanisms, strategies and plans for replicating and scaling gender interventions to advance gender equality and end all forms of discrimination against women and girls. This volume contains inspiring stories of VO-SACs in increasing women’s access to rights and entitlements, and other economic issues like addressing wage disparities between men and women in the village through collective action; addressing issues of drudgery; the labour rights of migrants, prevention of child marriage, increasing girls’ retention in schools, preventing child abuse, alcoholism, domestic violence, witch hunting, human trafficking, and COVID-related gender issues. Broadly, the case studies highlight how VO-SACs have used multiple strategies including restorative justice, collective action, offering support to women (including psycho-social support) and sometimes even engaging with men to address issues that matter to women.
Gender-based violence – Causes and consequences
Violence against women and girls has long been a barrier to their equal participation in and contribution to society. Any and every form of violence against women – physical, mental, verbal, psychological or emotional – is a violation of their human rights, has severe and long-term impacts on survivors, their families and communities, and also affects social and economic development (García-Moreno et al., 2015; UN Women, 2020). There are multiple ways in which violence is experienced by women, several contexts in which it occurs, and thus, its costs and consequences are widespread (Day et al., 2005).
The issue becomes even more complicated when we account for the fact that it is not just men who inflict violence upon women but women as well, who can equally be perpetrators. This becomes relevant in a traditional society such as India’s where violence against women is not merely a gender issue. For far too long women have been responsible for the suffering of other women, especially in domiciliary settings where the triggers for violence are often women’s handling of domestic chores and responsibilities, increased mobility or greater financial independence. In this blog, I talk about what feminist literature has to say about the violence inflicted on women and girls by the opposite gender, and whether it has any correlation with women’s participation in the labour force along with their desire to be economically independent.
The ameliorative hypothesis on violence (Xie et al., 2012; Heirigs and Moore, 2018) is the most well-understood and logically coherent theory on the subject suggesting that as societies become more equal, violence decreases. The improved status of women relative to men, greater gender equality and a higher ratio of women to men in the labour force would in theory break traditions and reduce stereotypes that support the domination of women by men. This would lead to lower rates of violence against women, and ultimately empower women.
However, evidence on violence supports the backlash hypothesis. It argues that improvement in women’s relative socioeconomic status actually increases their rate of victimisation – a sharp contrast to the ameliorative hypothesis. With initial reductions in gender inequality in a society, men tend to find means to reassert their diminishing patriarchal power and authority and resist the increased power of women (Avakame, 1999). A narrowing gender gap as women advance in status and break down their traditional gender roles, acts as a threat for men and results in the ‘backlash effect’ (Xie et al., 2012). Given the setup of the Indian society and its strong patriarchal norms, men are conditioned to retain the identity of a provider, protect women of the household, and control decision-making in the family such that women conform to roles defined by traditions. The backlash hypothesis is particularly found to have more significant influence on domestic violence and intimate partner violence rather than on stranger violence or violence by known or unknown offenders (Xie et al., 2012).
Yet another argument that predicts women’s victimisation is the one offered by the lifestyle and routine activities theory. This theoretical strand of the literature suggests that absolute increases in women’s labour force participation are associated with increase in their victimisation by strangers and known others (Xie et al., 2012). Although the result predicted by this theory is similar to that of the backlash hypothesis, the reason is different. The lifestyle theory states that an increase in women’s labour force participation puts them at heightened risk of victimization by strangers due to greater exposure at work or in other out-of-home activities. The routine activities approach focuses on women’s changing activity patterns to determine how vulnerable they could be. In establishing the theory, Xie et al. (2012) also argue that while women’s access to resources (indicated by gains in education, income) can help them protect themselves from victimization, greater labour force participation increases exposure to victimization.
Historically and globally, women have experienced violence, irrespective of their age, wealth status, class, race, ethnicity, caste or religion, and even across settings – inflicted by their partner, children, family members, members of the neighborhood, community or workplace (UN Women, 2020). Among the many costs of violence against women – borne by the survivor, her household and society over time – is her participation in the labour force. A woman’s decision to join the labour force is a rational decision wherein she attempts to either maximise her own utility function or her households’ total welfare (Mehrotra and Parida, 2017). She compares the net benefit of joining the workforce to the net benefit of not doing so while also accounting for the cost of joining. The prevalence of violence against women in public spaces, public transport, neighborhood or at the workplace and the possibility of being abused contribute negatively to this equation, adding to the cost of participation in the workforce (Chakraborty et al., 2014; Satyam and Pickup, 2018). As a result, women are discouraged and make suboptimal labour supply decisions.
The malaise of inflicting violence against women and girls becomes more pronounced and relevant in India as we look closely at the reasons for women’s declining labour force participation over the last three decades. Research from various country settings has established that the fall in women’s labour force participation rate can be attributed to factors like – availability of care for children, elderly and specially abled; role of women in domestic and kinship settings along with long-standing patriarchal norms; occupational segregations and poor growth in female-friendly jobs; lack of infrastructure; concerns around safety and mobility; and sociocultural barriers and social identities (Chaudhary, 2021). In some way or the other, all of these play a role in the Indian context. An OECD report from the G20 Osaka Summit in 2019 stated that women in India are less likely to be employed than in other G20 countries, next only to Saudi Arabia (Satyam and Pickup, 2018).
In recent times, India’s female labour force participation rate has declined from 31.2 per cent (Employment-Unemployment Survey, 2011) to 23.3 per cent (Periodic Labour Force Survey, 2017), while the country-wide rate of crimes against women and girls has tripled from 18.8 per cent to 57.9 per cent during this period (as per National Crime Records Bureau).
IWWAGE is undertaking a state-level analysis to determine how women’s labour force participation rate has changed with the incidence of crimes against women between 2011 and 2017. It uses the ‘Crime in India’ statistics produced by the National Crime Records Bureau and looks at crimes that might serve as barriers to work, in this case, those that prevent women from stepping out to work and paint a perception of lack of safety. These include rape, kidnapping and abduction, sexual harassment and molestation.
A detailed report will be released soon. Watch out for the second part of this blog where I would unpack the report’s findings.
Neelanjana Gupta, Senior Research Associate at IWWAGE, is an economist with interest in evidence-based solutions to challenging questions of public policy. She works on areas of human development and social inclusion.
References
Avakame, Edem F. “Females’ labor force participation and rape: An empirical test of the backlash hypothesis.” Violence Against Women 5.8 (1999): 926-949.
Chakraborty, Tanika, et al. “Crime and Women’s Labor Force Participation.” (2014).
Chaudhary, Ruchika. Working or Not: What Determines Women’s Labour Force Participation in India? IWWAGE, 2021.
Day, Tanis, Katherine McKenna, and Audra Bowlus. “The economic costs of violence against women: An evaluation of the literature.” United Nations (2005): 1-66.
García-Moreno, Claudia, et al. “Addressing violence against women: a call to action.” The Lancet 385.9978 (2015): 1685-1695.
Heirigs, Mark H., and Matthew D. Moore. “Gender inequality and homicide: a cross-national examination.” International Journal of Comparative and Applied Criminal Justice 42.4 (2018): 273-285.
Mehrotra, Santosh, and Jajati K. Parida. “Why is the labour force participation of women declining in India?.” World Development 98 (2017): 360-380.
Satyam, Nishtha, and Francine Pickup. “To Reverse Decline of Women in Labour Force, India Must Make Its Working Spaces Safe.” The Wire (2018).
UN Women. “COVID-19 and Violence against Women and Girls: Addressing the Shadow Pandemic.” Policy Brief 17 (2020).
Xie, Min, Karen Heimer, and Janet L. Lauritsen. “Violence against women in US metropolitan areas: Changes in women’s status and risk, 1980–2004.” Criminology 50.1 (2012): 105-143.